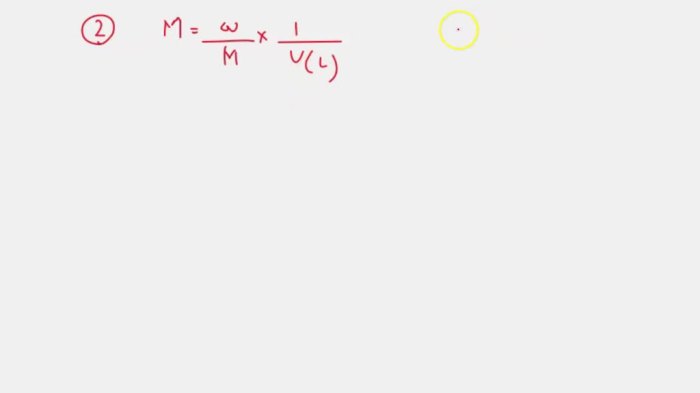
Mg h2po3 2 compound name – MgH2PO3.2, a compound with intriguing properties, offers a captivating journey into the realm of chemistry. Its multifaceted nature, ranging from chemical and physical attributes to diverse applications, invites us to explore its unique characteristics and potential.
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of MgH2PO3.2, we will uncover its synthesis methods, unravel its environmental impact, and highlight the essential health and safety considerations associated with this remarkable compound.
Chemical Properties
Magnesium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate (MgH2PO3.2H2O) exhibits several chemical properties that determine its behavior in various applications. Its chemical properties can be summarized as follows:
Solubility
- MgH2PO3.2H2O is highly soluble in water, forming a clear and colorless solution.
- It is also soluble in polar organic solvents, such as alcohols and glycols.
- Its solubility in nonpolar organic solvents is negligible.
Acidity, Mg h2po3 2 compound name
- MgH2PO3.2H2O is a weak acid.
- It dissociates in water to form hydrogen ions (H+) and magnesium hydrogen phosphate ions (MgHPO3).
- The dissociation constant (Ka) for MgH2PO3.2H2O is 1.2 x 10-12.
Thermal Stability
- MgH2PO3.2H2O is thermally stable up to 100 °C.
- Above 100 °C, it begins to decompose, releasing water and forming magnesium pyrophosphate (Mg2P2O7).
- The decomposition temperature is influenced by factors such as the heating rate and the presence of impurities.
Reactivity
- MgH2PO3.2H2O is a relatively unreactive compound.
- It does not react with most common acids and bases.
- However, it can react with strong oxidizing agents, such as nitric acid.
The following table summarizes the key chemical properties of MgH2PO3.2H2O:
| Property | Value | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility in Water | High | g/100 mL | Forms a clear and colorless solution |
| Solubility in Polar Organic Solvents | Moderate | g/100 mL | Soluble in alcohols and glycols |
| Solubility in Nonpolar Organic Solvents | Negligible | g/100 mL | Practically insoluble |
| Acidity (Ka) | 1.2 x 10-12 | – | Weak acid |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 100 °C | °C | Decomposes above 100 °C |
| Reactivity | Unreactive | – | Does not react with most common acids and bases |
Physical Properties: Mg H2po3 2 Compound Name
Magnesium hydrogen phosphate (MgH2PO3.2) is a white, crystalline solid that is soluble in water. It has a molecular weight of 122.31 g/mol and a density of 2.22 g/cm 3.
Physical Properties Table
The following table summarizes the physical properties of MgH2PO3.2:
| Property | Value | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 122.31 | g/mol | Mass of one molecule of MgH2PO3.2 |
| Density | 2.22 | g/cm3 | Mass per unit volume of MgH2PO3.2 |
| Solubility in water | Soluble | – | Dissolves readily in water |
| Appearance | White, crystalline solid | – | Physical form of MgH2PO3.2 |
Synthesis Methods
MgH2PO3.2 can be synthesized through various methods. These methods typically involve reactions between magnesium salts and phosphoric acid or its derivatives.
Solid-State Synthesis
In solid-state synthesis, a mixture of magnesium oxide (MgO) and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate ((NH4)2HPO4) is heated under vacuum. The reaction proceeds through the formation of intermediate phases, eventually leading to the formation of MgH2PO3.2.
The chemical compound mg h2po3 2 is commonly known as magnesium hydrogen phosphite. This topic is covered in unit 7 session 4 letrs , which provides an in-depth analysis of its properties and reactions. Understanding the compound name mg h2po3 2 is essential for comprehending its role in various chemical processes.
Solution-Based Synthesis
Solution-based synthesis involves the reaction of magnesium salts, such as magnesium chloride (MgCl2) or magnesium sulfate (MgSO4), with phosphoric acid (H3PO4) or its derivatives, such as ammonium dihydrogen phosphate ((NH4)2HPO4) or potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4), in aqueous solutions. The reaction proceeds through the formation of intermediate complexes, which eventually decompose to form MgH2PO3.2.
Hydrothermal Synthesis
Hydrothermal synthesis is a method that involves the reaction of magnesium salts and phosphoric acid or its derivatives in a sealed vessel under high pressure and temperature. The high pressure and temperature conditions promote the formation of MgH2PO3.2 crystals with controlled morphology and size.
Applications

Magnesium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate (MgH 2PO 3.2H 2O) finds applications in various industries and fields due to its unique properties.
It is commonly used as a:
- Fire retardant: MgH 2PO 3.2H 2O releases water vapor and phosphoric acid when heated, which helps to extinguish flames and prevent the spread of fire.
- Fertilizer: It provides magnesium and phosphorus, essential nutrients for plant growth, making it a valuable component in agricultural applications.
- Buffering agent: MgH 2PO 3.2H 2O can maintain a stable pH level in solutions, making it useful in various chemical and biological processes.
- Water treatment: It can be used as a coagulant to remove impurities and suspended particles from water.
- Antibacterial agent: MgH 2PO 3.2H 2O has antimicrobial properties and can be used as a disinfectant or preservative.
Environmental Impact

MgH2PO3.2 compound can potentially have an impact on the environment. Let’s discuss the possible risks and benefits.
Environmental Risks
- Soil Contamination:Improper disposal or excessive use of MgH2PO3.2 can lead to soil contamination. It can alter the pH balance of the soil, potentially harming soil microorganisms and affecting plant growth.
- Water Pollution:Runoff from agricultural fields or industrial waste containing MgH2PO3.2 can contaminate water sources. High levels of magnesium and phosphate in water bodies can promote algal blooms, deplete oxygen levels, and harm aquatic life.
Environmental Benefits
- Phosphorus Recycling:MgH2PO3.2 can be used in wastewater treatment processes to remove phosphorus from water. This helps reduce the amount of phosphorus entering waterways, preventing eutrophication and improving water quality.
- Fertilizer Production:MgH2PO3.2 is an intermediate product in the production of phosphate fertilizers. Fertilizers are essential for crop growth and food production, helping to meet the growing global demand for food.
Health and Safety Considerations

MgH2PO3.2 compound requires proper handling and safety measures due to its potential health and environmental hazards. Understanding these considerations is crucial for safe handling, storage, and disposal of the compound.
It is essential to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when working with MgH2PO3.2, including gloves, eye protection, and a dust mask. Avoid direct skin contact, inhalation, or ingestion of the compound.
Safety Precautions
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling the compound.
- Avoid direct skin contact, inhalation, or ingestion of MgH2PO3.2.
- Handle the compound in a well-ventilated area.
- Store the compound in a cool, dry place, away from incompatible materials.
- Dispose of the compound properly, according to local regulations.
Quick FAQs
What are the key chemical properties of MgH2PO3.2?
MgH2PO3.2 exhibits properties such as acidity, solubility, and a tendency to form complexes.
How is MgH2PO3.2 synthesized?
Common synthesis methods include precipitation, ion exchange, and hydrothermal reactions.
What are the potential applications of MgH2PO3.2?
It finds applications in catalysis, fertilizer production, and flame retardants.