Construct a binomial probability distribution with the given parameters. – Constructing a binomial probability distribution with given parameters is a fundamental concept in statistics. It provides a framework for understanding the probability of observing a specific number of successes in a sequence of independent experiments with a constant probability of success.
This guide will delve into the definition, construction, applications, visualization, and limitations of the binomial probability distribution, equipping you with a comprehensive understanding of this essential statistical tool.
1. Define Binomial Probability Distribution
A binomial probability distribution is a discrete probability distribution that describes the number of successes in a sequence of independent experiments, each of which has a constant probability of success.
The key characteristics of a binomial distribution are:
- The number of trials, n, is fixed.
- The probability of success, p, is constant for each trial.
- The trials are independent, meaning the outcome of one trial does not affect the outcome of any other trial.
2. Constructing a Binomial Probability Distribution
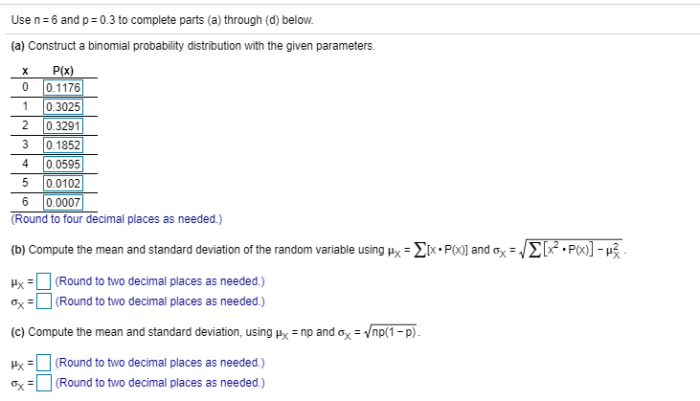
The formula for constructing a binomial probability distribution is:
P(X = x) = (n! / (x!(n-x)!))
- p^x
- (1-p)^(n-x)
where:
- P(X = x) is the probability of getting x successes in n trials.
- n is the number of trials.
- x is the number of successes.
- p is the probability of success on each trial.
3. Applications of Binomial Probability Distribution

The binomial probability distribution is used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Quality control
- Medical testing
- Marketing research
- Financial modeling
4. Visualizing a Binomial Probability Distribution: Construct A Binomial Probability Distribution With The Given Parameters.

A binomial probability distribution can be visualized using a histogram or a probability mass function (PMF).
The histogram shows the probability of each possible number of successes, while the PMF shows the probability density function for the distribution.
The shape of the binomial distribution depends on the values of n and p.
- For small values of n, the distribution is skewed to the right.
- For large values of n, the distribution is approximately normal.
- For values of p close to 0 or 1, the distribution is skewed to the left or right, respectively.
5. Limitations of Binomial Probability Distribution
The binomial probability distribution has several limitations, including:
- It assumes that the trials are independent.
- It assumes that the probability of success is constant for each trial.
- It is only applicable to discrete random variables.
In situations where these assumptions are not met, other probability distributions may be more appropriate.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the formula for constructing a binomial probability distribution?
The formula is P(X = k) = (n choose k) – p^k – (1-p)^(n-k), where n is the number of trials, p is the probability of success, and k is the number of successes.
What are the key characteristics of a binomial distribution?
It is discrete, bounded, skewed to the right for p > 0.5 and skewed to the left for p< 0.5, and has a mean of np and variance of np(1-p).
When is a binomial distribution appropriate?
It is appropriate when the number of trials is fixed, the probability of success is constant, and the trials are independent.